Low Carb Bread and Blood Sugar What You Need to Know

Low carb bread is a great option if you’re looking to reduce your carbohydrate intake without giving up the comfort of eating bread. Whether you’re focused on managing blood sugar levels, avoiding energy crashes, or simply maintaining steady glucose levels, low carb bread can make a difference. For those with diabetes, insulin resistance, or anyone aiming for healthier blood sugar management, this bread can offer a practical solution. Traditional bread, made with refined flour, tends to cause quick spikes in blood sugar due to its high carb content. In contrast, low carb bread made from ingredients like almond flour, coconut flour, and flaxseed meal offers a healthier alternative. But how exactly does low carb bread affect blood sugar?
In this article, we’ll explore how low carb bread impacts blood glucose levels, especially for those who are mindful of their blood sugar. We’ll also dive into specific types, such as sourdough low carb bread, and explain how the fiber and lactobacillus culture in sourdough contribute to better blood sugar regulation.
What Is Low Carb Bread?

Low-carb bread refers to any bread made from ingredients that are lower in carbohydrates than traditional wheat-based breads. Unlike white bread, which is made from highly refined flour that breaks down into sugar rapidly, low-carb bread is made with healthier alternatives, such as almond flour, coconut flour, flaxseed meal, or psyllium husk. These ingredients not only reduce the carbohydrate content but also increase the bread’s fiber content, which can help slow down sugar absorption.
Different types of low-carb bread include:
- Low-carb loaf: A loaf made with low-carb flours like almond or coconut flour.
- Carb-conscious bread: Specifically designed to reduce carbohydrate intake while still maintaining a satisfying texture and flavor.
- Diabetic-friendly bread: Bread that is made with minimal carbs and often includes additional healthy ingredients to assist in blood sugar management.
For people concerned with maintaining healthy blood sugar levels, low-carb bread is a great option that allows them to enjoy bread without spiking their glucose levels.
How Does Low Carb Bread Affect Blood Sugar Levels?
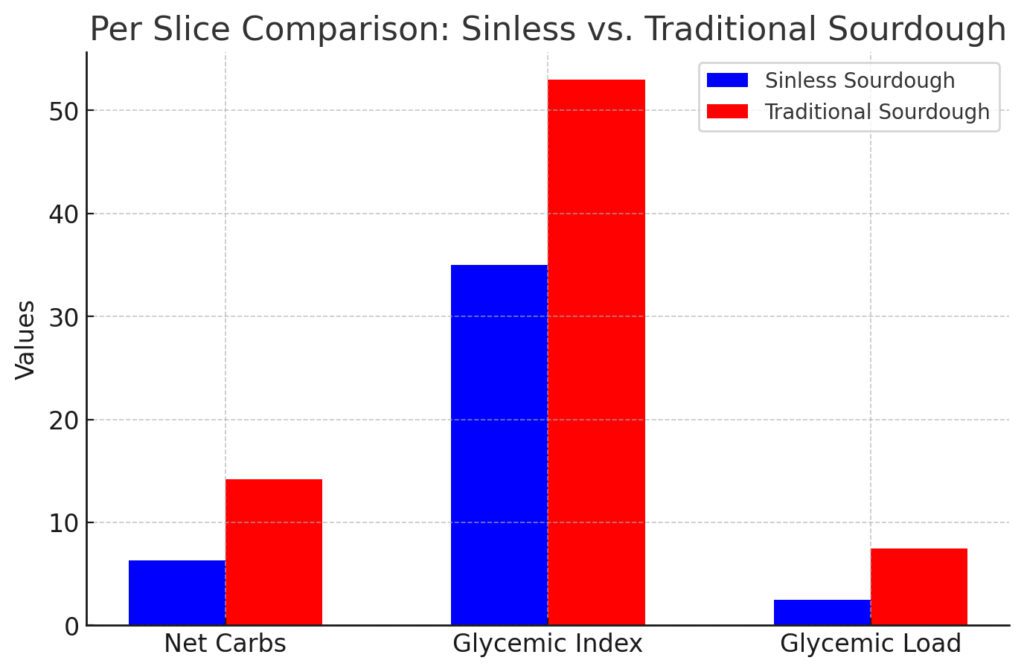
Understanding how low-carb bread affects blood sugar is key for anyone looking to manage their glucose levels. Let’s break it down:
1. Slower Sugar Absorption
One of the main advantages of low-carb bread is its ability to slow down sugar absorption into the bloodstream. Unlike traditional white bread, which is digested quickly and causes blood sugar spikes, low-carb bread made with fiber-rich ingredients like almond flour or coconut flour digests more slowly. This helps regulate the release of glucose into the bloodstream, preventing sharp blood sugar spikes.
For individuals with insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes, this slower absorption is critical in preventing long-term complications related to blood sugar management.
2. Lower Glycemic Index
The glycemic index (GI) measures how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels. Low glycemic bread, made from low-carb ingredients, has a much lower GI than traditional bread. This means that low-carb bread won’t cause the same rapid increase in blood glucose as conventional breads made from wheat or refined flour.
For example, low-net-carb bread made with coconut flour or almond flour generally has a much lower glycemic index, offering a more stable and controlled blood sugar response. The lower GI of these breads helps maintain consistent energy levels throughout the day without triggering the typical sugar crash associated with high-carb foods.
3. High Fiber Content
Fiber plays a crucial role in blood sugar control. It slows the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, leading to more gradual increases in blood glucose. Many low-carb breads are high in fiber due to ingredients like flaxseed meal, chia seeds, and psyllium husk. These fibers not only help stabilize blood sugar but also support digestive health.
Since fiber-rich bread has minimal impact on blood sugar levels, it’s an excellent option for those looking to manage blood glucose more effectively, while also supporting overall health. A high fiber content also contributes to satiety, helping prevent overeating and unnecessary insulin spikes.
How Does Sourdough Low Carb Bread Affect Blood Sugar Levels?

Sourdough low-carb bread offers several unique benefits for blood sugar management. Let’s explore how sourdough low-carb bread affects blood glucose and why it’s an excellent choice for those managing blood sugar levels.
1. The Fermentation Process and Blood Sugar Control
The fermentation process used to make sourdough involves the breakdown of sugars by naturally occurring wild yeasts and bacteria. This process helps lower the glycemic index of the bread. For sourdough low-carb bread, this effect is even more pronounced due to the use of low-carb flours like almond flour or coconut flour.
The fermentation process can also reduce the presence of phytates—compounds found in grains that can hinder nutrient absorption and contribute to blood sugar spikes. As a result, sourdough low-carb bread has a more controlled effect on blood sugar compared to regular sourdough made with wheat flour.
2. Glycemic Index of Sourdough Low Carb Bread
Sourdough bread naturally has a lower glycemic index than many other breads due to its unique fermentation process. When combined with low-carb ingredients, this effect is amplified, resulting in a bread that has a minimal impact on blood sugar levels.
This means that sourdough low-carb bread is a better option for those looking to avoid blood sugar spikes. For individuals with diabetes or insulin resistance, this bread provides a slow and steady release of glucose into the bloodstream, helping to maintain stable blood sugar levels throughout the day.
3. The High Fiber Content of Sourdough Low Carb Bread
An often-overlooked benefit of sourdough low-carb bread is its high fiber content. Many low-carb sourdough recipes incorporate fiber-rich ingredients such as flaxseed meal, chia seeds, and psyllium husk. Fiber is essential for controlling blood sugar because it slows the absorption of carbohydrates and helps regulate insulin levels.
The high fiber in sourdough low-carb bread further supports stable blood sugar levels. By delaying the digestion of starches and sugars, fiber ensures that glucose enters the bloodstream more gradually, which is particularly beneficial for people with type 2 diabetes or anyone trying to maintain balanced blood sugar levels.
4. Prebiotic Benefits of Sourdough
The fermentation process in sourdough also creates prebiotics—compounds that promote the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. A healthy gut microbiome has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and blood sugar regulation. By incorporating sourdough low-carb bread into your diet, you may be supporting not only your blood sugar levels but also your digestive health.
5. Acidity of Sourdough and Blood Sugar Response
Sourdough’s naturally occurring lactic acid can help further control blood sugar by reducing the speed at which starches and sugars are broken down. This acidity slows down the conversion of carbohydrates into glucose, leading to a slower and more controlled blood sugar response.
6. Benefits for Insulin Sensitivity
Studies have shown that sourdough bread can improve insulin sensitivity, making it an excellent choice for individuals with insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes. Low-carb sourdough bread, due to its combination of fermentation, low-carb ingredients, and high fiber content, can provide even more benefits by reducing insulin resistance and helping the body process sugar more efficiently.
Can I Bake Low Carb Sourdough At Home?

Absolutely! Baking your own low-carb sourdough bread at home is not only possible but also quite rewarding. While traditional sourdough bread relies on high-carb flours, there are now innovative ways to create the same tangy, chewy goodness without the excess carbohydrates. With the right ingredients and techniques, you can enjoy authentic low-carb sourdough that fits perfectly into your health-conscious lifestyle.
The best part is that baking low-carb sourdough is more achievable than you might think, and you don’t have to compromise on taste or texture. Whether you’re following a low-carb or keto diet, baking your own bread ensures you can control the ingredients and make a loaf that works with your blood sugar management goals.
FYI: SOURDOUGH MEDICAL STUDIES AND REVIEWS:
Here they are:
- Does Sourdough Bread Provide Clinically Relevant Health Benefits?: Link: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10399781/
- The Sourdough Microbiome : Link: https://asm.org/articles/2020/june/the-sourdough-microbiome
- Sourdough Microbiome Comparison and Benefits: Link: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8306212/
- Nutritional Benefits of Sourdough; Systematic Review : Link: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36811591/
- Use of sourdough in low FODMAP baking : Link: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29932101/
Disclaimer:
All information provided on this website regarding the health benefits of sourdough low carb bread is intended for educational purposes only. The content presented is not meant to be taken as specific medical advice for any individual. It should not be considered a replacement for professional medical guidance or treatment. If you have any health concerns, especially related to diabetes, pre-diabetes, or any other medical condition, please consult with a healthcare professional immediately.
🔥 UNLOCK MORE RECIPES STARTER + MEMBERSHIP – Only $99 CAD! 🔥
Get a second starter with your membership – the exclusive membership recipes use 2 different low-carb feedings to bake the 3 different styles of breads and baked goods (weight loss, low-carb lifestyle maintenance, fast and easy discard recipes) that will transform your baking game beyond what your current starter can achieve!
💰 PRICING: Regular Price: $198 CAD Today Only: $99 CAD (Only $99 CAD!)
SINLESSSOURDOUGH.COM
Click the Starter + Membership Box
Your Discounted Membership Includes:
🥖 1849 San Francisco Gold Rush Dehydrated Starter: Scientifically validated starter shipped free to your door!
📦 FREE Shipping: Your starter ships to you at no extra cost
🎥 25+ Instructional Video Trainings: Master Keto & Low-Carb Sourdough Baking with comprehensive video lessons
📚 3 E-Sinless Sourdough Cookbooks: Easy-to-follow sourdough recipes for your low-carb lifestyle
📖 3 E-Keto Low-Carb Cookbooks: Delicious low-carb recipes to complement your baking
🗓️ E-28-Day Keto Kickstarter Journal & Planner: Stay on track with your low-carb journey
📝 Keto Low-Carb E-Cheat Sheets & Quick Guides: Shortcuts for perfect baking every time
🍞 Training for 3 Styles of Keto & Low-Carb Sourdough: Learn recipes for weight loss, lifestyle maintenance, and easy discard recipes
💬 Exclusive Community Access: Share tips, ask questions, and get expert support from fellow bakers
🚀 DON’T MISS OUT – GRAB IT FOR Only $99 CAD NOW! 🚀
Transform Your Baking Today:
- Visit sinlesssourdough.com™
- Click “Starter + Membership”
- Proceed to the purchase page
- Enter code: SINLESS50
- Complete checkout and START BAKING guilt-free sourdough immediately!
SINLESSSOURDOUGH.COM
Click the Starter + Membership Box












Responses